
What is Edge Computing?
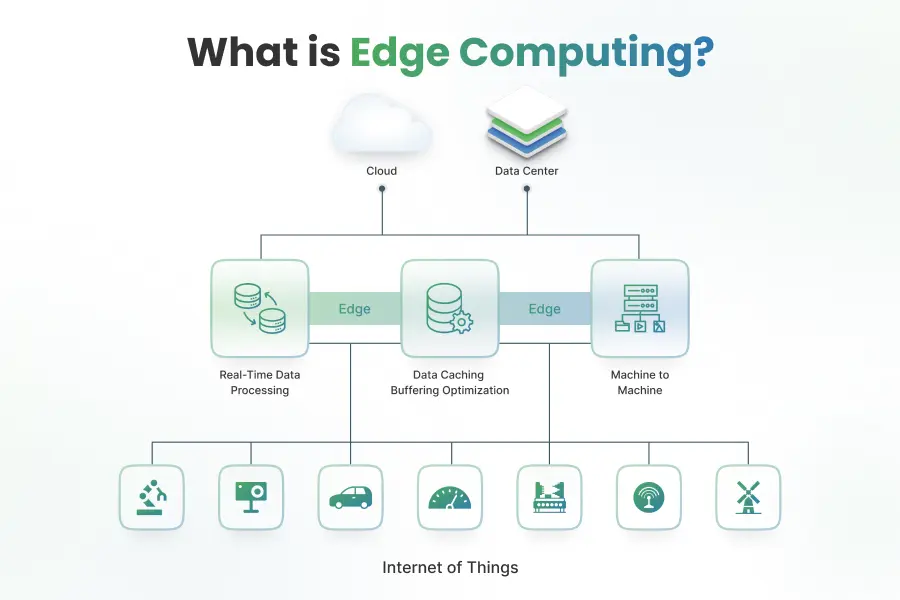
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, which is typically the edge of the network. In traditional cloud computing, data is sent to a centralized data center for processing, but with edge computing, the processing is done on local devices or servers, closer to the source of the data.
Edge computing is designed to address the limitations of cloud computing in terms of latency, bandwidth, and privacy. By moving processing and storage closer to the edge, edge computing reduces the time it takes for data to travel back and forth between the source and the cloud, resulting in lower latency and faster response times. This is particularly important for applications that require real-time data processing, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and remote monitoring.
The Benefits of Edge Computing
There are several key benefits to adopting edge computing:
1. Reduced Latency
One of the main advantages of edge computing is reduced latency. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing eliminates the need to send data to a remote data center for processing. This results in faster response times, which is critical for applications that require real-time data analysis and decision-making. For example, in autonomous vehicles, split-second decisions need to be made to ensure the safety of the passengers and other road users.
2. Bandwidth Optimization
Edge computing also helps optimize bandwidth usage by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud. Instead of sending raw data to the cloud for processing, edge devices can perform initial data filtering and analysis, and only send relevant information to the cloud. This reduces the strain on the network and can result in significant cost savings, especially in scenarios where large amounts of data are generated, such as in IoT deployments.
3. Improved Reliability
Another benefit of edge computing is improved reliability. By distributing computing and storage capabilities across multiple edge devices, the system becomes more resilient to failures. Even if one edge device fails, the others can continue to operate, ensuring that critical applications and services remain available. This is particularly important in mission-critical environments, such as healthcare, where downtime can have serious consequences.
4. Enhanced Data Privacy
Edge computing also enhances data privacy by keeping sensitive data closer to the source. In traditional cloud computing, data is sent to a remote data center for processing, which raises concerns about data privacy and security. With edge computing, sensitive data can be processed locally, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Edge-to-Cloud Computing
While edge computing brings computation and storage closer to the source of the data, it does not eliminate the need for cloud computing. In fact, edge computing and cloud computing can work together in a complementary manner, forming a hybrid architecture known as edge-to-cloud computing.
In an edge-to-cloud architecture, edge devices perform initial data processing and analysis, and only send relevant information to the cloud for further processing and storage. This allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both edge computing and cloud computing. Edge computing provides low-latency processing and real-time decision-making capabilities, while cloud computing offers scalability, advanced analytics, and long-term storage.
Edge-to-cloud computing is particularly useful in scenarios where a large amount of data is generated at the edge, such as in industrial IoT deployments. Edge devices can filter and aggregate the data, and send only the most relevant information to the cloud for analysis. This reduces the bandwidth requirements and allows organizations to focus their cloud resources on high-value tasks, such as predictive maintenance and advanced analytics.

Edge Devices
Edge devices are the key components of edge computing infrastructure. They are the devices that perform computation and data processing at the edge of the network. Edge devices can range from small sensors and actuators to more powerful devices such as gateways and edge servers.
Edge devices are typically equipped with sensors, processors, and storage capabilities, allowing them to collect data, analyze it, and make decisions in real-time. They are designed to operate in resource-constrained environments, with limited power, memory, and processing capabilities. Some examples of edge devices include:
1. Sensors and Actuators
Sensors and actuators are the basic building blocks of edge computing. They are used to collect data from the physical world and control physical processes. Sensors can measure various parameters such as temperature, pressure, humidity, and motion, while actuators can control devices such as motors, valves, and switches. These devices are often deployed in large numbers to monitor and control industrial processes, smart buildings, and environmental conditions.
2. Gateways
Gateways are devices that bridge the gap between edge devices and the cloud. They act as intermediaries, collecting data from edge devices and sending it to the cloud for further processing and storage. Gateways can perform data aggregation, filtering, and protocol translation, allowing different types of edge devices to communicate with each other and with the cloud. They are often used in IoT deployments to connect edge devices to the internet and enable remote management and monitoring.
3. Edge Servers
Edge servers are more powerful devices that can perform complex data processing and analysis at the edge. They are typically deployed in locations such as factories, retail stores, and remote sites where low-latency processing is required. Edge servers can run applications and services locally, eliminating the need to send data to a remote data center. They can also act as gateways, aggregating data from multiple edge devices and sending it to the cloud.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a powerful paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the source of the data. It offers several benefits, including reduced latency, optimized bandwidth usage, improved reliability, and enhanced data privacy. Edge computing can be combined with cloud computing in an edge-to-cloud architecture to leverage the benefits of both approaches. Edge devices, such as sensors, gateways, and edge servers, are the key components of edge computing infrastructure. They enable real-time data processing and decision-making at the edge of the network, making edge computing a critical enabler for applications such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and remote monitoring.
Ready to get started?
Unlock opportunities: Contact Us, Partner with Us and boost your revenue.